
-Collective effects in High density regime.
·
Laser ablation in
solid targets
o Cluster formation
o Mass analysis of yields
·
Multiphoton
ionization in gas jet
o Collective effects in high density regime
o Ion acceleration
-Anomalous Saturation of Ion yields vs Laser Intensity
due to electron-ion trapping at various gas density in Ar.
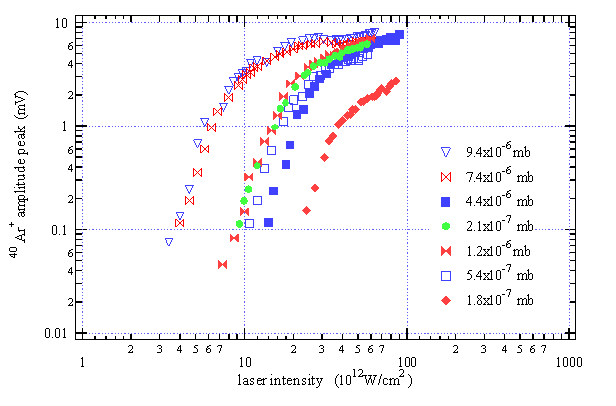
Curves
correspond to different gas densities given in millibar.
-In
the absence of electron-ion interactions, curves should be parallel and
linearly dependent on the gas density as it occurs at a signal <=1 mV.
-The
electron-ion trapping, which depends on the absolute charge density produced by
laser, screens the external electric field and prevent ions from collection. It
leads to an apparent saturation of the signal that does not corresponds to
the saturation of ionization.
-Mutual interactions among ion clouds.
36Ar and 40Ar
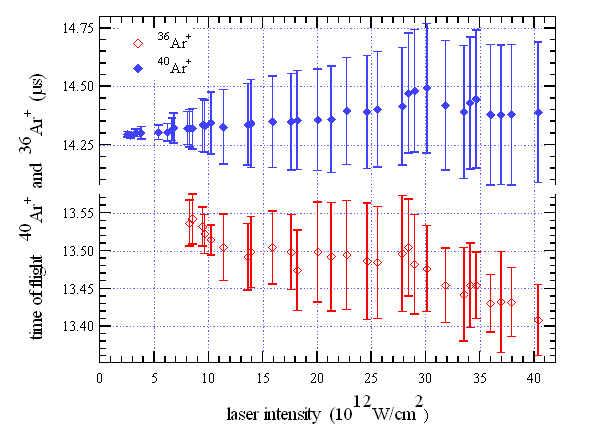
§
Due to interaction by repulsive electrostatic forces the
cloud containing a lighter isotope accelerates (-134 ns), while the cloud with
the heavier isotope slows
(+198 ns).
§
By increasing the ion density the difference in the
time of arrival increases due to the growing mutual repulsion between clouds
but the ion signals do not overlap.
§
This effect can be exploited to enhance the isotope
separation in high gas density regime.